Grown in South America (Peru, Chile and Bolivia) for thousands of years, Quinoa is non-GMO, gluten-free and usually grown organically.
Quinoa belongs to the same family as the sugar beet and spinach. It is a useful little plant. Its leaves can be eaten like spinach but its seeds can also be used in the same way as grain. It technically isn’t a cereal grain, but a pseudo-cereal (non-grassy plant used in much the same way as cereals and grains with a similar nutritional profile).
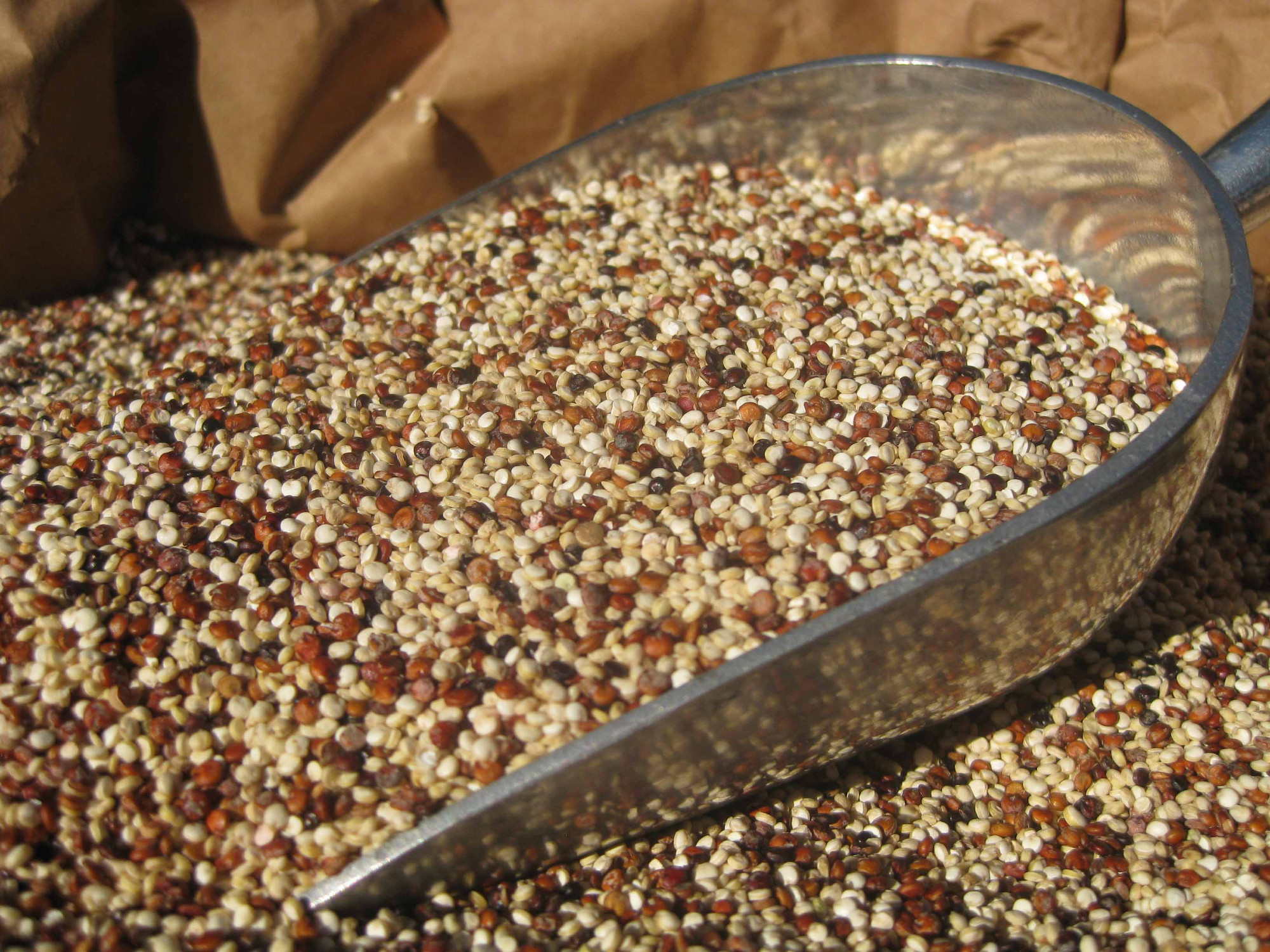
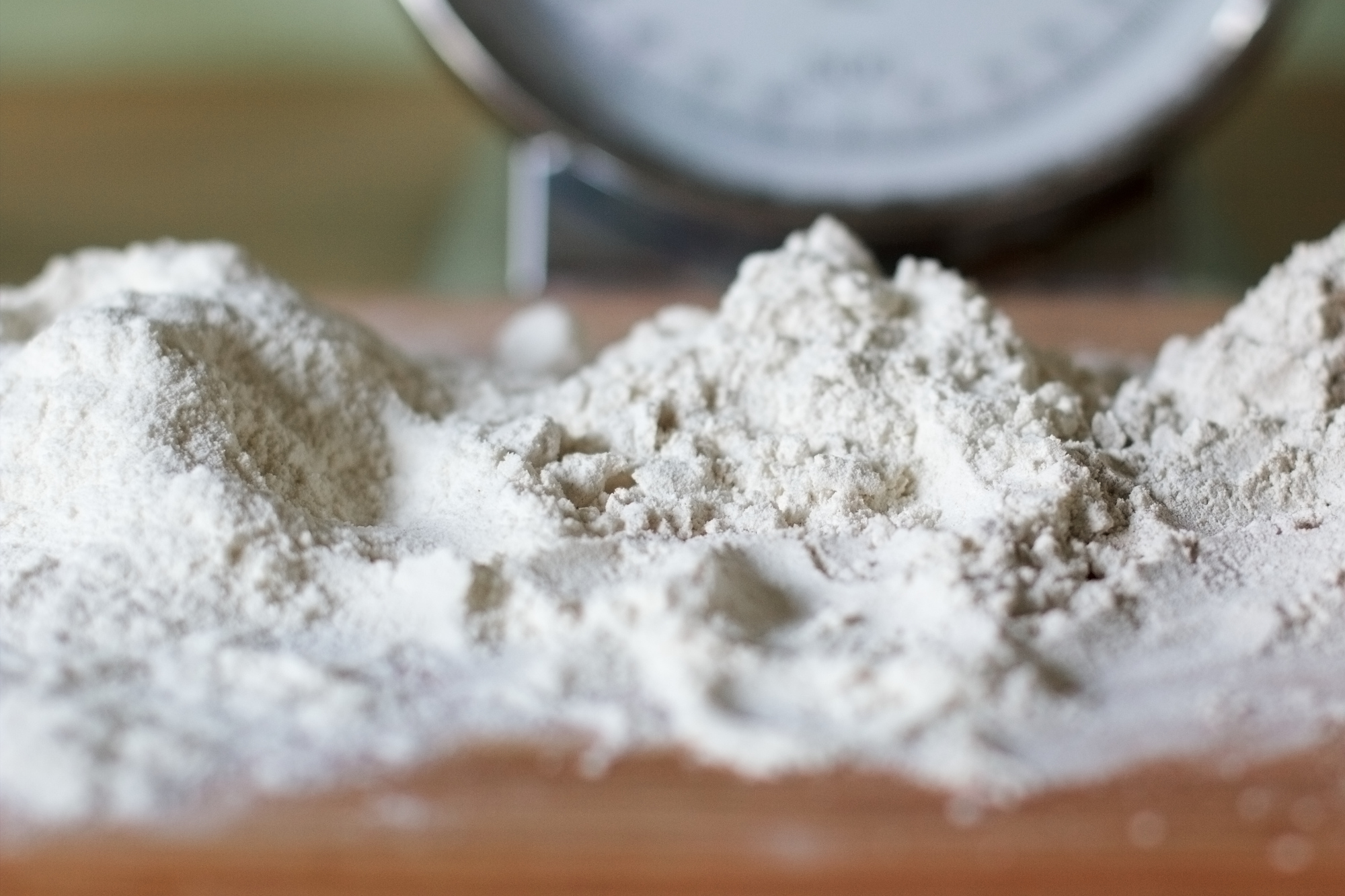
Although there are hundreds of cultivated types of quinoa, the most common versions available in stores are white, red, and black quinoa used as grains or transformed into flour and flakes.
Quinoa is high in anti-inflammatory phytonutrients, which make it potentially beneficial for human health in the prevention and treatment of disease. Quinoa contains small amounts of the heart healthy omega-3 fatty acids and has a higher content of monounsaturated fat.
As a complete protein, quinoa contains all nine essential amino acids. Naturally high in dietary fibre, quinoa is a slowly digested carbohydrate.
For this reason, it is recommended to consume 48 grams of whole grains per day.
In the last few years, Quinoa has become very trendy among health conscious people.
Available varieties:
- White, red and black Quinoa, conventional and organic;
- Quiona meal;
- Flakes Quinoa conventional and organic.